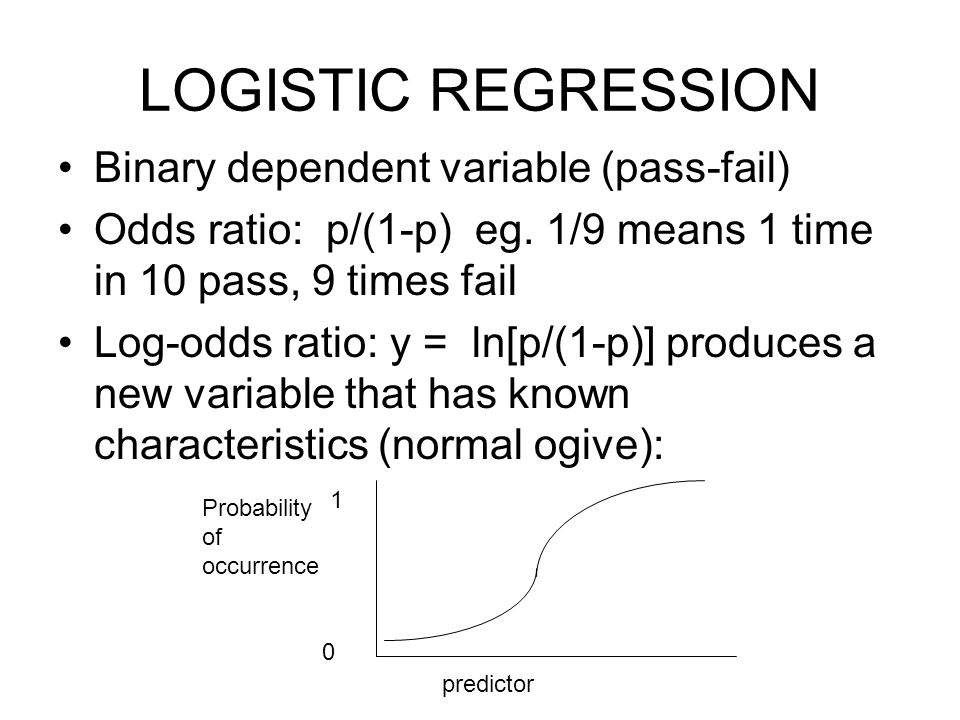
Class center, middle, inverse, titleslide # Logistic regression ## Model Predictions & Assumptions ### Prof Maria Tackett ### 0330 class middle, centerLogistic regression helps us estimate a probability of falling into a certain level of the categorical response given a set of predictors We can choose from three types of logistic regression, depending on the nature of the categorical response variable For binary logistic regression, the odds of success are \(\begin{equation*}Jan 24, 17 · The survival probability is if Pclass were zero (intercept) However, you cannot just add the probability of, say Pclass == 1 to survival probability of PClass == 0 to get the survival chance of 1st class passengers Instead, consider that the logistic regression can be interpreted as a normal regression as long as you use logits
Logistic Regression
Odds probability logistic regression
Odds probability logistic regression-Jun 22, · In the previous tutorial, you understood about logistic regression and the best fit sigmoid curve Next, discuss Odds and Log Odds Odds The relationship between x and probability is not very intuitive Let's modify the above equation to find an intuitive equation Step1 Calculate the probability of not having blood sugar Step2 WhereJul 02, · If p is a probability, then p/(1 − p) is the corresponding odds;


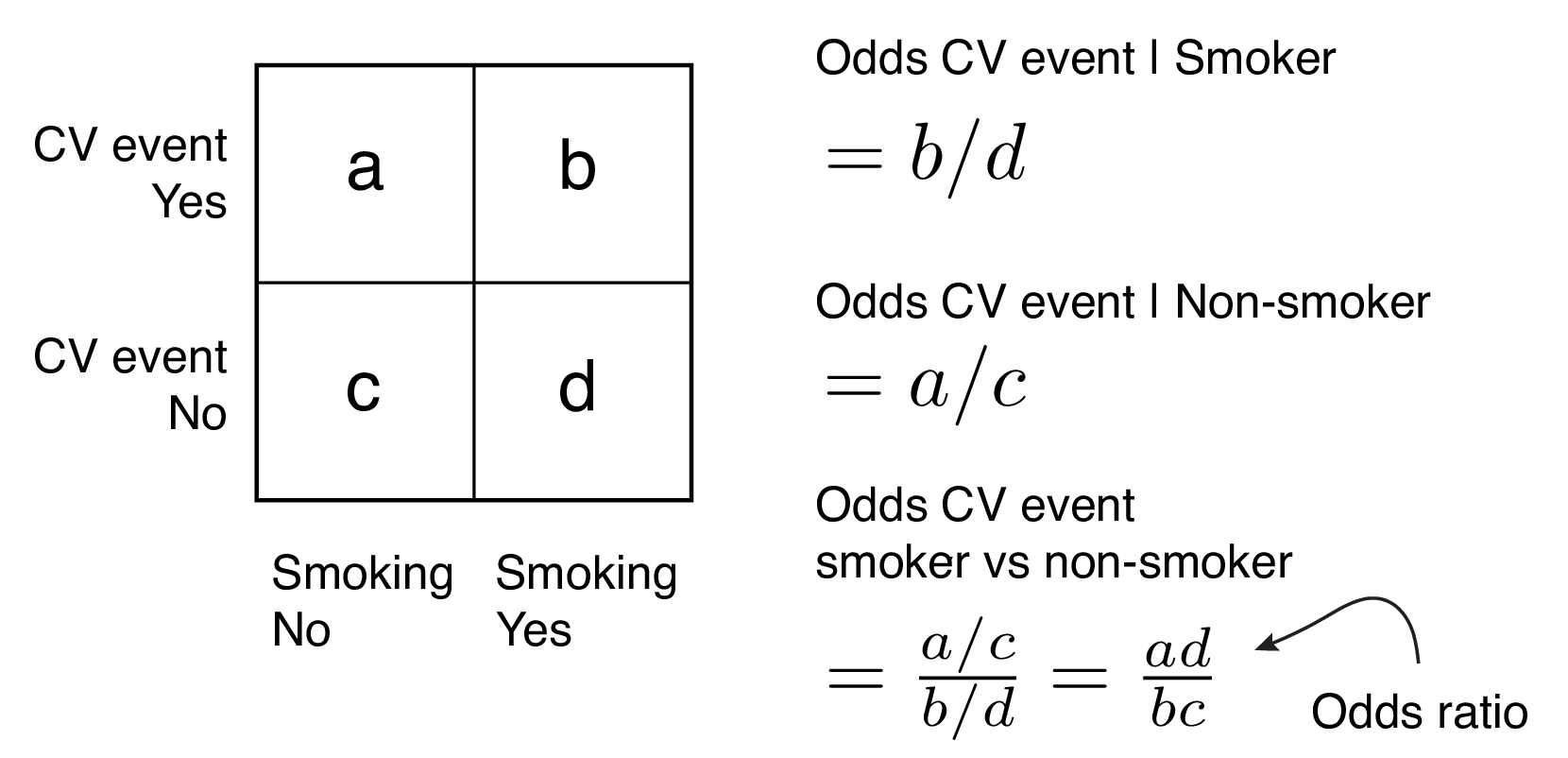
Logistic Regression Binary Dependent Variable Pass Fail Odds Ratio P 1 P Eg 1 9 Means 1 Time In 10 Pass 9 Times Fail Log Odds Ratio Y Ln P 1 P Ppt Download
In order to understand a logistic regression, we should first understand several concepts odds, odds ratio, logit odds, and p\൲obability, and the relationships among all the concepts Let's first explain what is odds, and what is probability In logistic對 regression, odds meansLast class we discussed how to determine the association between two categorical variables (odds ratio, risk ratio, chisquare/Fisher test) Suppose we want to explore a situation in which the dependent variable is dichotomous (1/0, yes/no, case/control) andNote that z is also referred to as the logodds because the inverse of the sigmoid states that z can be defined as the log of the
The above formula to logits to probabilities, exp (logit)/ (1exp (logit)), may not have any meaning This formula is normally used to convert odds to probabilities However, in logistic regression an odds ratio is more like a ratio between two odds values (which happen to already be ratios)G A Barnard in 1949 coined the commonly used term logodds;Jun 01, 12 · Binary, Ordinal, and Multinomial Logistic Regression for Categorical Outcomes Understanding Probability, Odds, and Odds Ratios in Logistic Regression They're both free The former describes multinomial logistic regression and how interpretation differs from binary The latter goes into more detail about how to interpret an odds ratio Karen
Thinking about log odds can be confusing, though So using the math described above, we can rewrite the simple logistic regression model to tell us about the odds (or even about probability) Odds = e β0β1*X Using some rules for exponents, we can obtain Odds = (e β0)*(e β1*X) When X equals 0, the second term equals 10A logistic regression model makes predictions on a log odds scale, and you can convert this to a probability scale with a bit of work Suppose you wanted to get a predicted probability for breast feeding for a year old mom The log odds would be3654*0157 = 0514 You need to convert from log odds to oddsApr 04, 21 · Logistic equation The function that converts logodds to probability is the logistic function and the unit of measurement for the logodds scale is called logit, which is from logistic unit (hence, the name) So from the equation above, ultimately, we try to predict the left path of the equation (not the right) because p(y=1x) is what we want So we can take the inverse of this


Obtaining And Interpreting Odds Ratios For Interaction Terms In Jmp



Cq1 Qoq Ufzylm
May 19, 15 · In a logistic regression model, odds ratio provide a more coherent solution as compared to probabilities Odds ratio represent the constant effect of an independent variable on a dependent variable Here, being constant means that this ratio does not change with a change in the independent (predictor) variableFeb 10, · where y' is the output of the logistic regression model for a particular example \(z = b w_1x_1 w_2x_2 \ldots w_Nx_N\) The w values are the model's learned weights, and b is the bias;142, 143 Logistic regression Often a xed change in x has less impact when ˇ(x) is near zero or one Example Let ˇ(x) be probability of getting an A in a statistics class and x is the number of hours a week you work on homework When x = 0, increasing x by 1 will change your (very small) probability of an A very little



How To Interpret Logistic Regression Coefficients Displayr
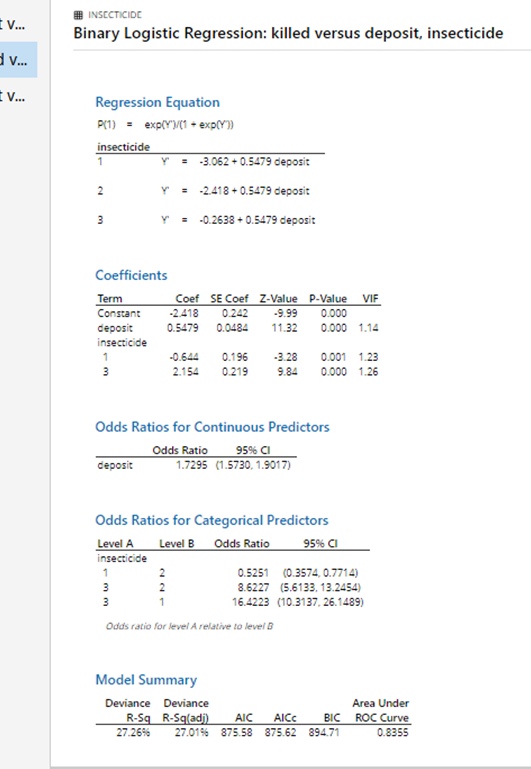


Ii Binary Logistic Regression Insecticides Xlsx Chegg Com
Intuitively (and mathematically), positive weights means that an increase in that covariate increases the probability of a positive response—and vice versa More rigorously, the coefficient is equal to the logodds ratio (can be derived from the lNow we can relate the odds for males and females and the output from the logistic regression The intercept of 1471 is the log odds for males since male is the reference group ( female = 0) Using the odds we calculated above for males, we can confirm this log(23) = 1470) This is sometimes called the logit transformation of the probability In the logistic regression model, the magnitude of the association of X and Y is represented by the slope β 1 Since X is binary, only two cases need be considered X = 0 and X = 1 The logistic regression model lets us define two quantities 𝑃𝑃0= Pr(𝑌𝑌= 1
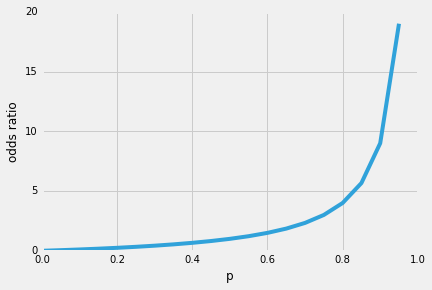


Logistic Regression Why Sigmoid Function


Multivariable Logistic Regression Results A Forest Plot Showing The Download Scientific Diagram
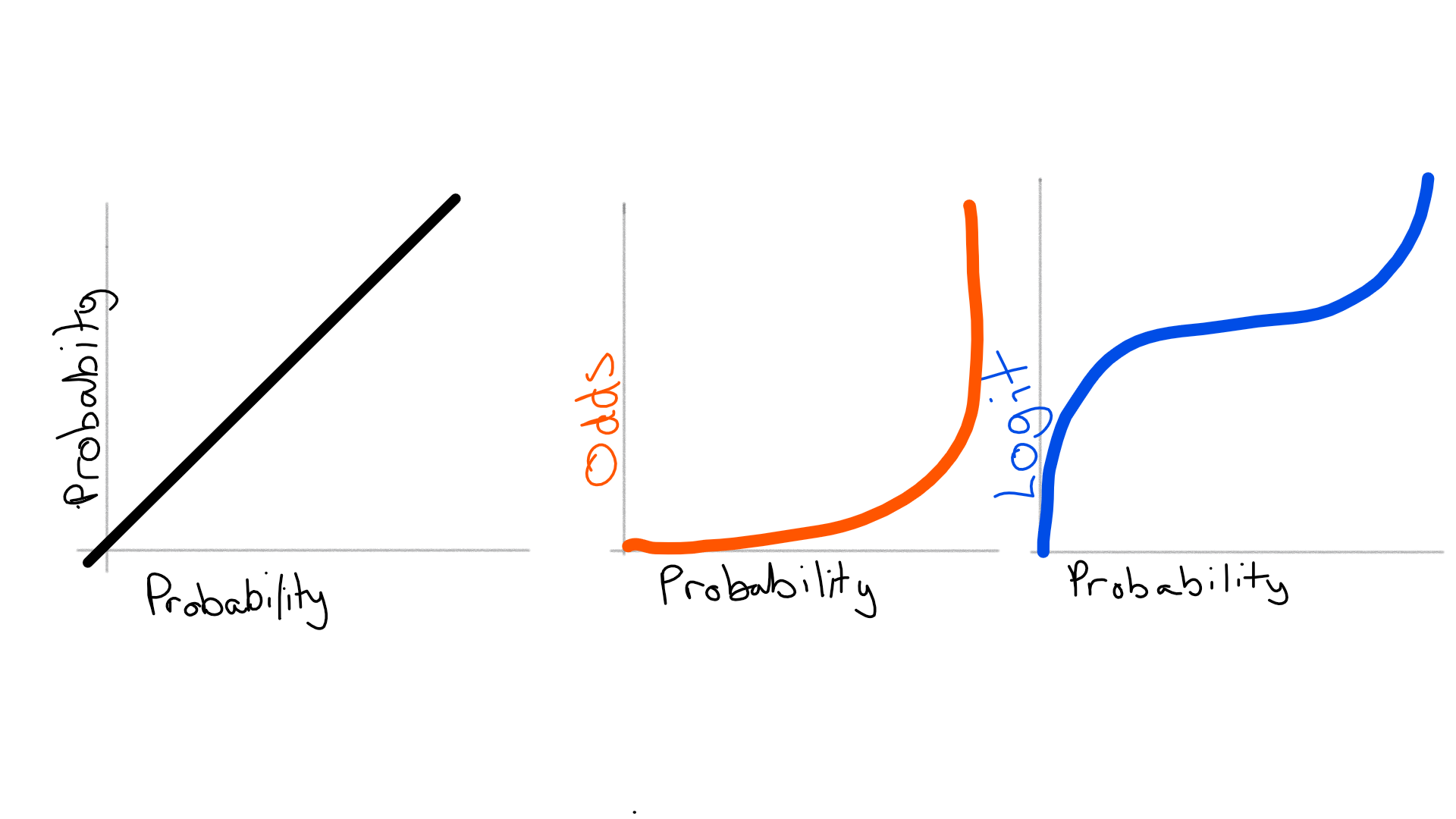
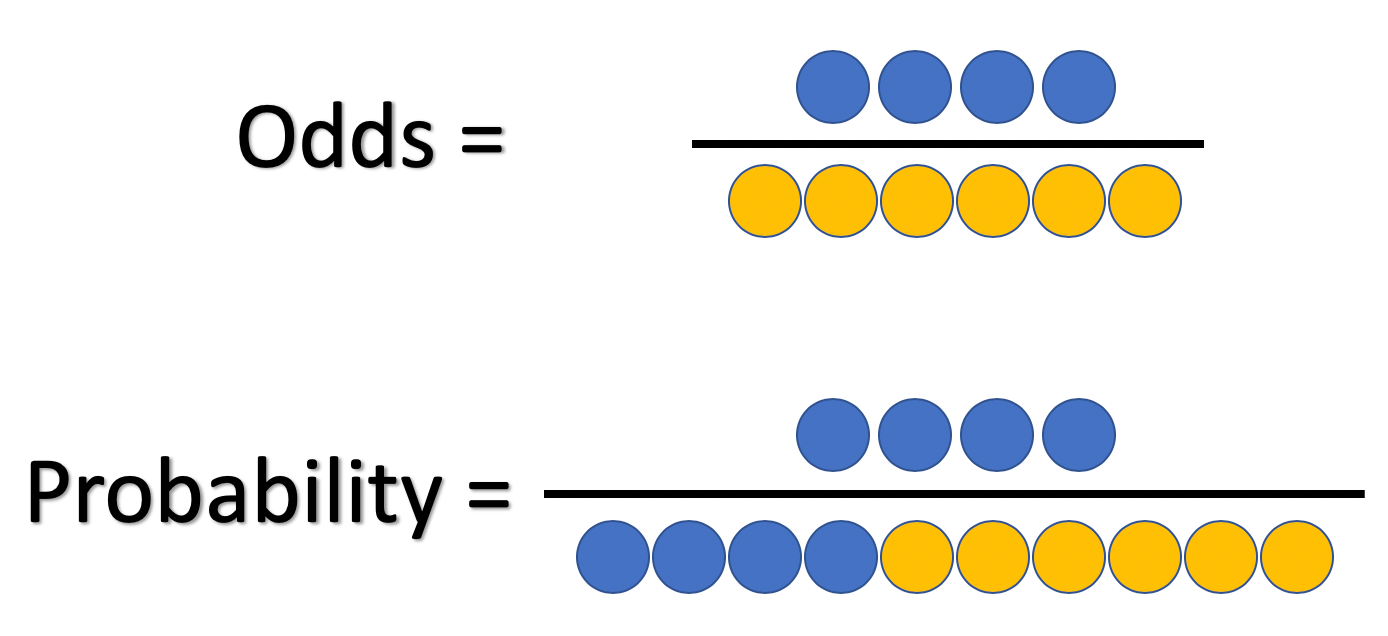
Oct 27, 17 · The probability that an event will occur is the fraction of times you expect to see that event in many trials Probabilities always range between 0 and 1 The odds are defined as the probability that the event will occur divided by the probability that the event will not occur If the probability of an event occurring is Y, then the probability of the event not occurring is 1YThe logodds of an event is the logit of the probability of the event Uses and properties The logit in logistic regression is a special case of a link function in a generalized linear model it is the canonical link function for the Bernoulli distributionMay 14, 21 · Fisher's Exact test calculates oddsratio Logistic regression What's next Further readings and references Source This post was inspired by two short Josh Starmer's StatQuest videos as the most intuitive and simple visual explanation on odds and logodds, oddsratios and logoddsratios and their connection to probability (you can watch



The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor
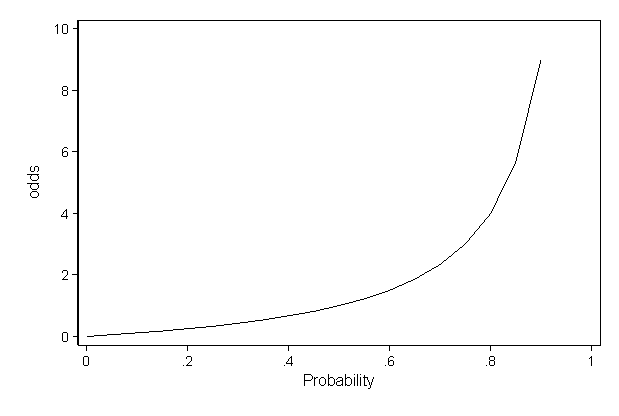


Faq How Do I Interpret Odds Ratios In Logistic Regression
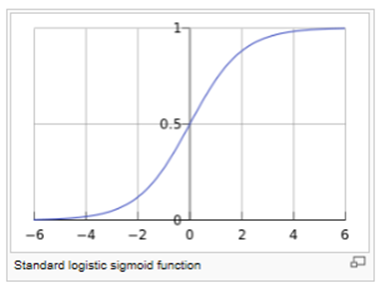
Aug 02, 19 · Logit To beginn with the Logit it is defined, as explained in the introduction, as the natual logarithm of the odds Odds are the ratio of the probability that the outcome variable will be 1 \(p(Y=1)\), also considered as the proabability of success, over the proabability that it will be 0 \(p(Y=0)\), sometimes considered as the probability of failureDefinition of the logistic function An explanation of logistic regression can begin with an explanation of the standard logistic functionThe logistic function is a sigmoid function, which takes any real input , and outputs a value between zero and one For the logit, this is interpreted as taking input logodds and having output probabilityThe standard logistic function → (,) isSep 26, 02 · Since logistic regression calculates the probability or success over the probability of failure, the results of the analysis are in the form of an odds ratio For example, logistic regression is often used in epidemiological studies where the result of the analysis is the probability of developing cancer after controlling for other associated


9 2 Binary Logistic Regression R For Health Data Science



Log Odds Interpretation Of Logistic Regression Youtube
Apr 22, 16 · The model that logistic regression gives us is usually presented in a table of results with lots of numbers The coefficients are on the logodds scale along with standard errors, test statistics and pvalues It can be difficult to translate these numbers into some intuition about how the model "works", especially if it has interactionsAge (in years) is linear so now we need to use logistic regression From the logistic regression model we get Odds ratio = 1073, p value < , 95% confidence interval (1054,1093) interpretation Older age is a significant risk for CAD For every one year increase in age the odds is 1073 times largerJan 05, 09 · I see a lot of researchers get stuck when learning logistic regression because they are not used to thinking of likelihood on an odds scale Equal odds are 1 1 success for every 1 failure 11 Equal probabilities are 5 1 success for every 2 trials Odds can range from 0 to infinity Odds greater than 1 indicates success is more likely than


Linear Vs Logistic Probability Models Which Is Better And When Statistical Horizons



Statquest Odds And Log Odds Clearly Explained Youtube
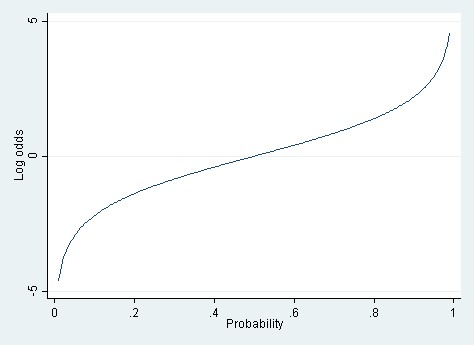
The logit of the probability is the logarithm of the odds, ie The "logistic" function of any number ∝In video two we review / introduce the concepts of basic probability, odds, and the odds ratio and then apply them to a quick logistic regression example UnThis video explains how the linear combination of the regression coefficients and the independent variables can be interpreted as representing the 'log odds'



Nhanes Tutorials Module 10 Logistic Regression



Logistic Regression Binary Dependent Variable Pass Fail Odds Ratio P 1 P Eg 1 9 Means 1 Time In 10 Pass 9 Times Fail Log Odds Ratio Y Ln P 1 P Ppt Download
An important property of odds ratios is that they are constant It does not matter what values the other independent variables take on For instance, say you estimate the following logistic regression model 1685 x 1 0039 x 2 The effect of the odds of a 1unit increase in x 1 is exp(1685) = 118 Meaning the odds increase by 18%Back to logistic regression In logistic regression, the dependent variable is a logit, which is the natural log of the odds, that is, So a logit is a log of odds and odds are a function of P, the probability of a 1 In logistic regression, we find logit(P) = a bX,Probabilities in logistic regression Prof Andrew Noymer Sociology 221 University of California, Irvine Preliminaries There is an odds ratio But there is no predicted probability (of 1 vs 0 on the outcome variable) for female


Logistic Regression


Logistic Regression Reporting Odds Ratios Youtube
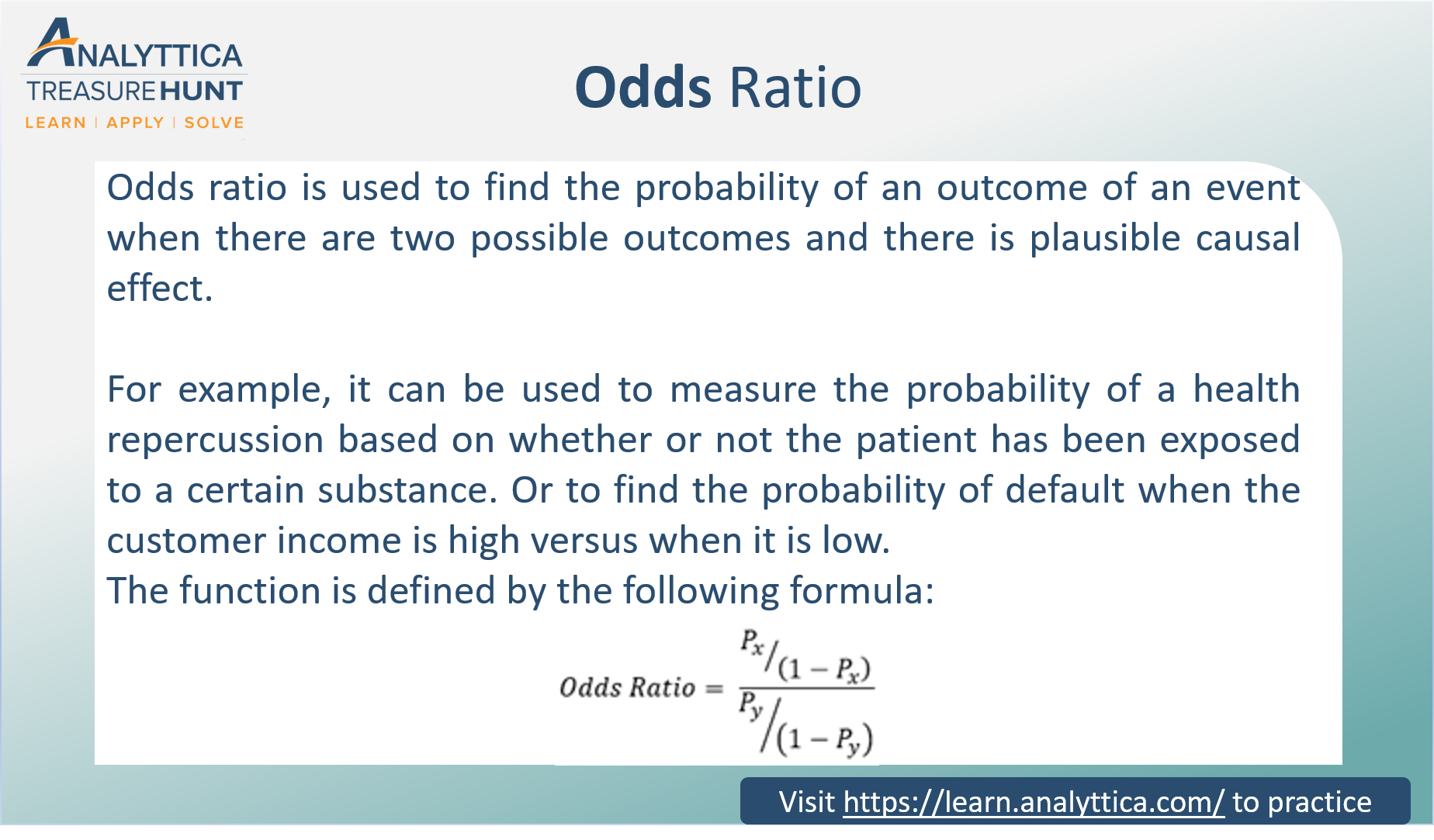
Feb , · Probability vs Odds vs Log Odds All these concepts essentially represent the same measure but in different ways In the case of logistic regression, log odds is used We will see the reason why log odds is preferred in logistic regression algorithmDec 31, 19 · Why do we need logistic regression Logistic regression predicts the probability of success A success vs failure can take a form of 1 vs 0, YES vs NO or TRUE vs FALSE While the success is always measured in only two (binary) values, either success or failure, the probability of success can take any value from 0 to 1 The probability ofMar 16, 21 · In statistics, an odds ratio tells us the ratio of the odds of an event occurring in a treatment group to the odds of an event occurring in a control group Odds ratios appear most often in logistic regression, which is a method we use to fit a regression model that has one or more predictor variables and a binary response variable An adjusted odds ratio is an odds ratio


Simple Logistic Regression


Chapter 5 Logistic Regression Hands On Machine Learning With R
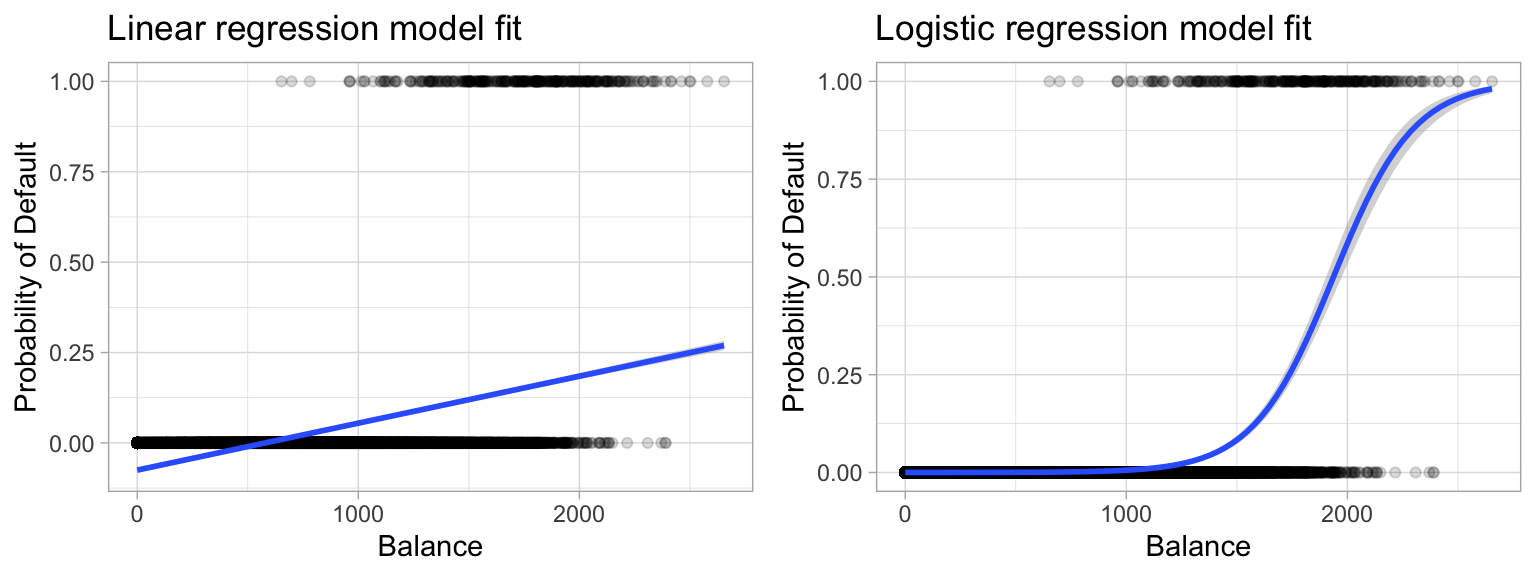
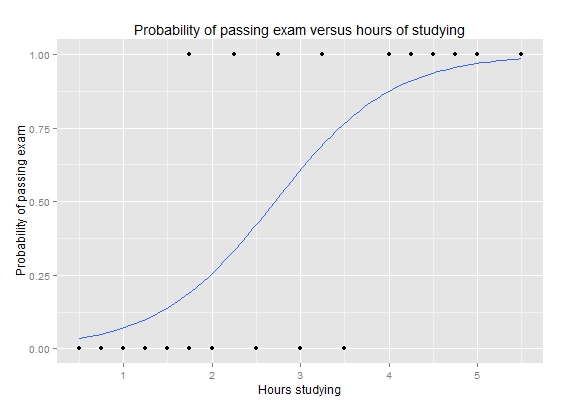
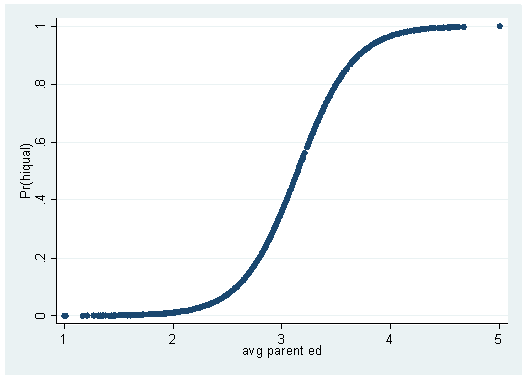
Jul 07, 12 · I have a question about plotting a probability curve for a logistic regression model that has multiple predictors I'm posted this here on SO because I'm wondering about ggplot2 specific solutions, and creating useful graphics from a logit model in ggplot2 So here is an example =Labs(title ="probability versus odds") 000 025 050 075 100 0 50 100 150 odds p probability versus odds Finally, this is the plot that I think you'llfind most useful because inlogistic regression81 Introduction to logistic regression Until now our outcome variable has been continuous But if the outcome variable is binary (0/1, "No"/"Yes"), then we are faced with a classification problem The goal in classification is to create a model capable of classifying the outcome—and, when using the model for prediction, new observations—into one of two categories



Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios


Logistic Regression Stata
Apr 21, 21 · Logistic Regression Odds = P/(1P) where P = probability of an event occurring, and (1P)= probability of the event not occurring In fact, a chisquared analysis will give us the same odds ratio and pvalue as the simple logistic regression, because smoking is the only independent variable This simple logistic regression and the chiThe x values are the feature values for a particular example;• Ordinal logistic regression (Cumulative logit modeling) • Proportion odds assumption • Multinomial logistic regression • Independence of irrelevant alternatives, Discrete choice models Although there are some differences in terms of interpretation of parameter estimates, the essential ideas are similar to binomial logistic regression
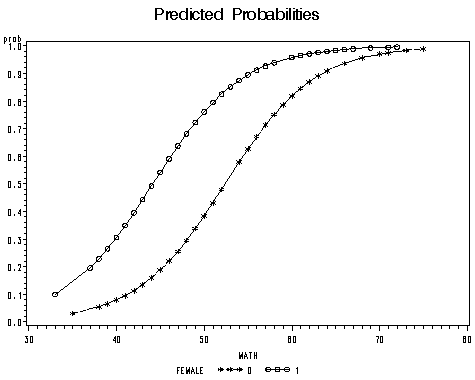


Proc Logistic And Logistic Regression Models
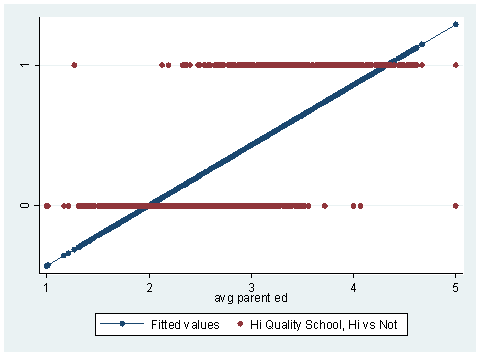


Logistic Regression With Stata Chapter 1 Introduction To Logistic Regression With Stata
71 Logistic Regression 711 Why use logistic regression?May 30, 16 · The logarithm of an odds can take any positive or negative value Logistic regression is a linear model for the log (odds) This works because the log (odds) can take any positive or negative number, so a linear model won't lead to impossible predictionsOct 05, 15 · There are several types of ordinal logistic regression models Probably the most frequently used in practice is the proportional odds model (Hosmer and Lemeshow, Applied Logistic Regression (2nd ed), p 297) Before we explain a "proportional odds model", let's just jump ahead and do it


Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios
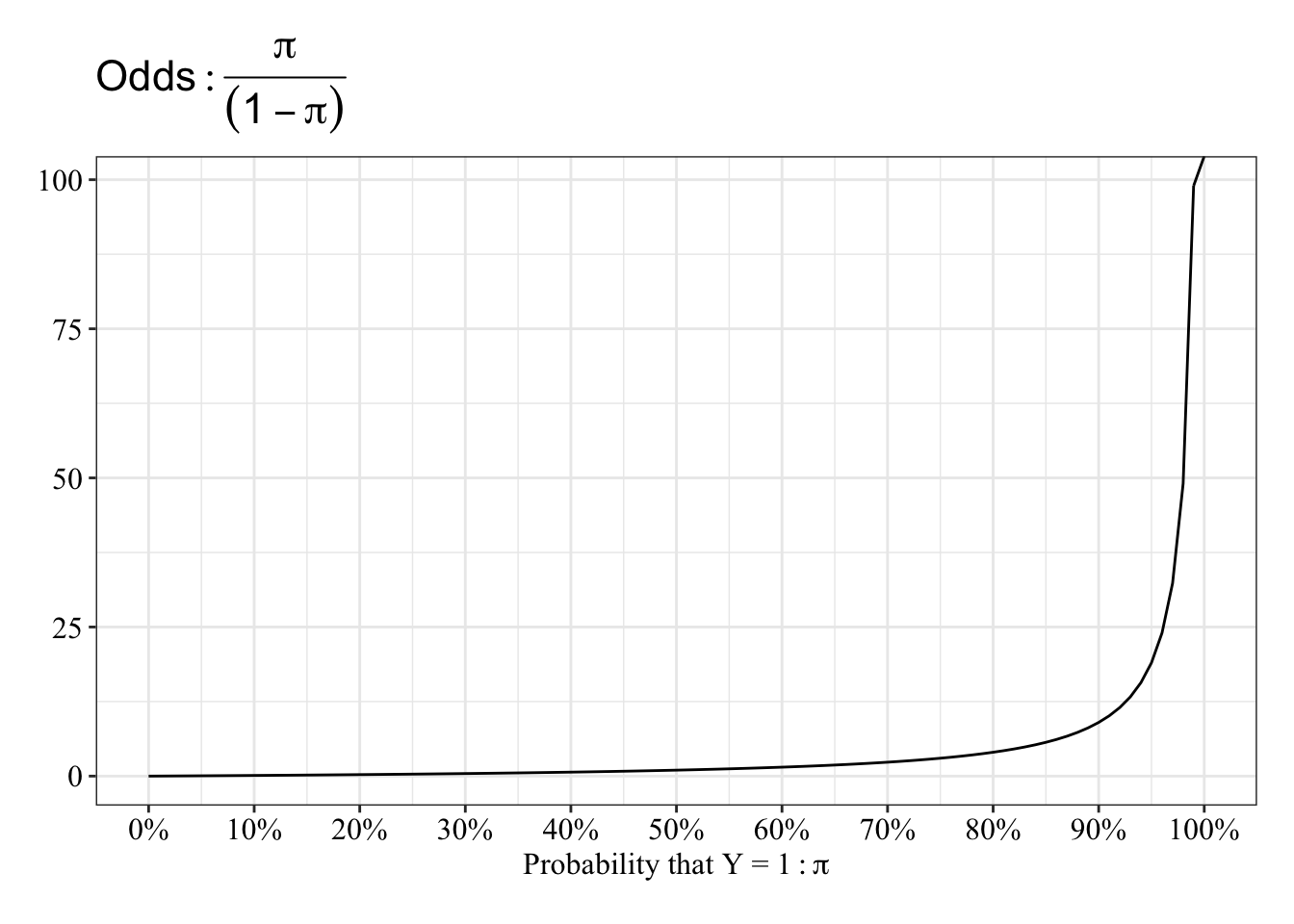


Logistic Regression In R Nicholas M Michalak
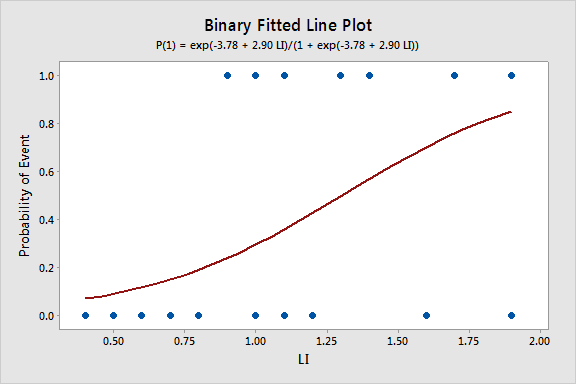


12 1 Logistic Regression Stat 462



Logit Of Logistic Regression Understanding The Fundamentals By Saptashwa Bhattacharyya Towards Data Science
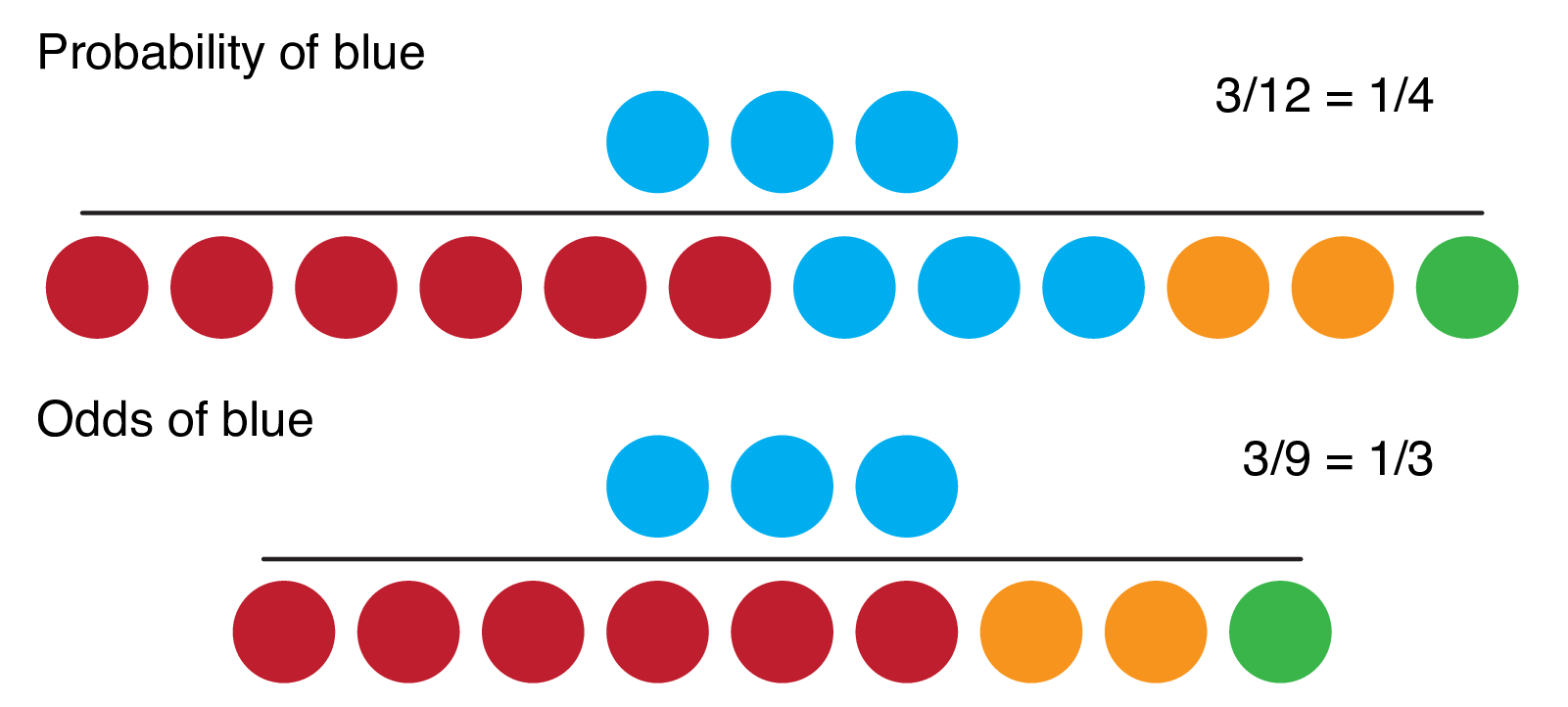


9 2 Binary Logistic Regression R For Health Data Science



Logistic Regression Estimates Odds Ratios Of The Probability Of Download Table



Logistic Regression
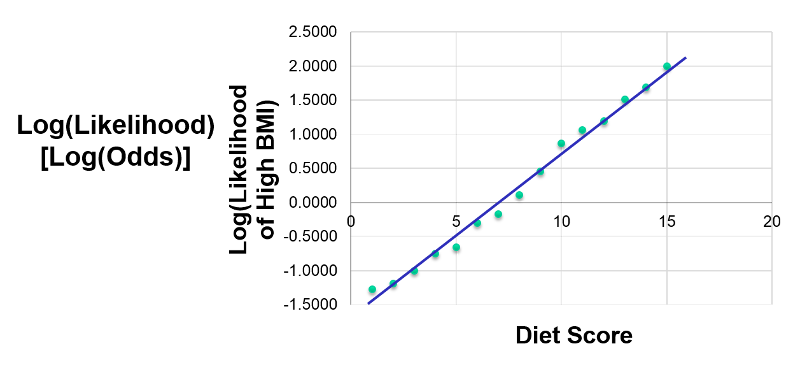


Multiple Logistic Regression Analysis



Logistic Regression Calculating A Probability
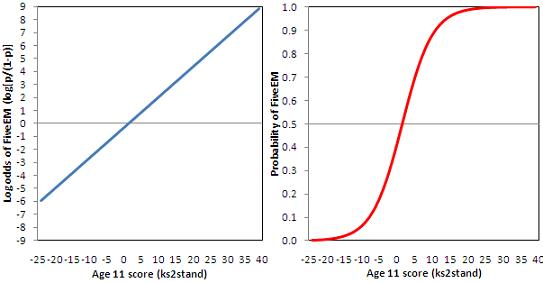


4 5 Interpreting Logistic Equations



How To Interpret The Weights In Logistic Regression By Mubarak Bajwa Medium


Logistic Regression Essentials In R Articles Sthda



Logistic Regression Data Vedas



What And Why Of Log Odds What Are Log Odds And Why Are They By Piyush Agarwal Towards Data Science



Logistic Regression 1 Sociology 11 Lecture 4 Copyright
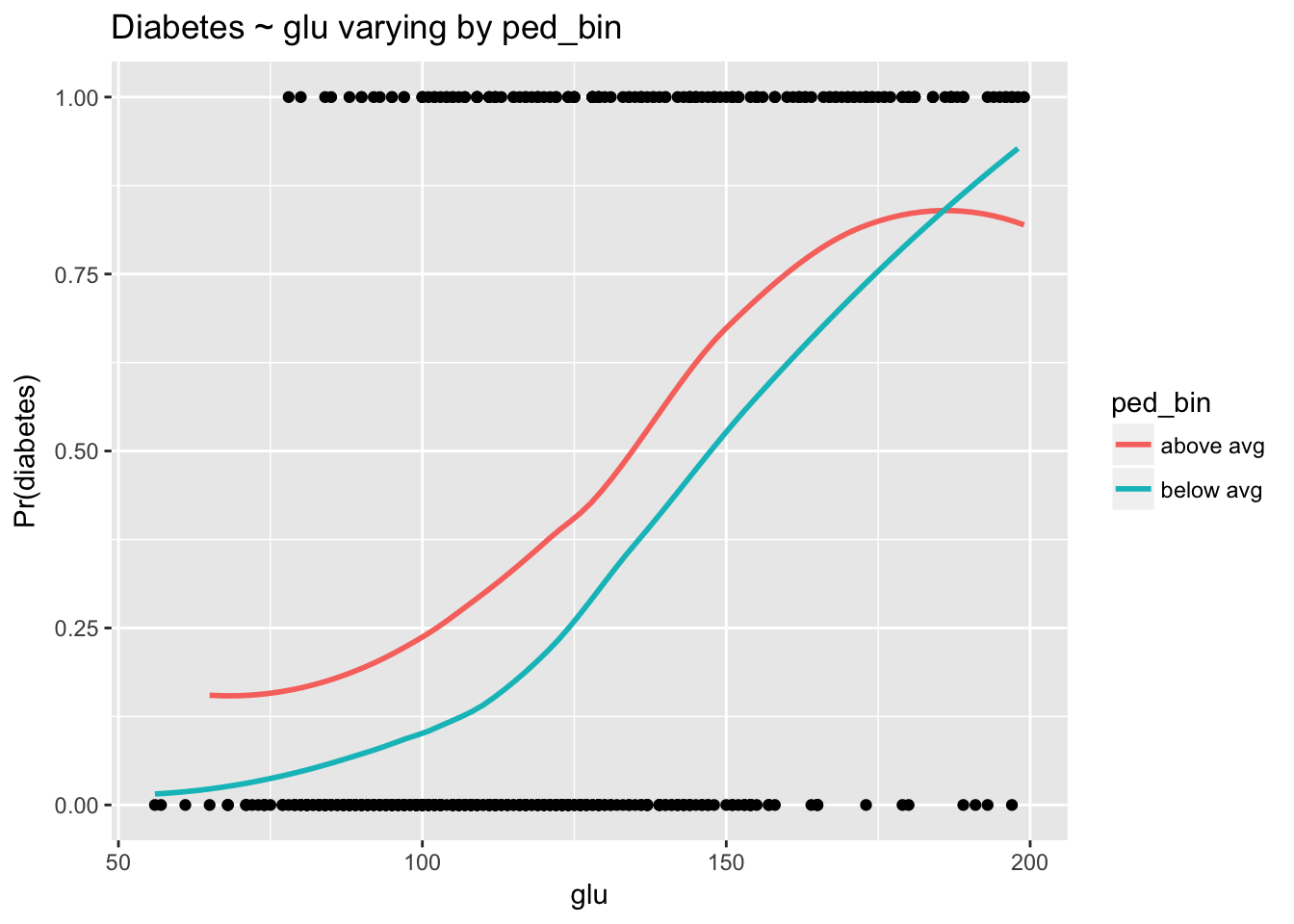


Course Notes For Is 64 Statistics And Predictive Analytics
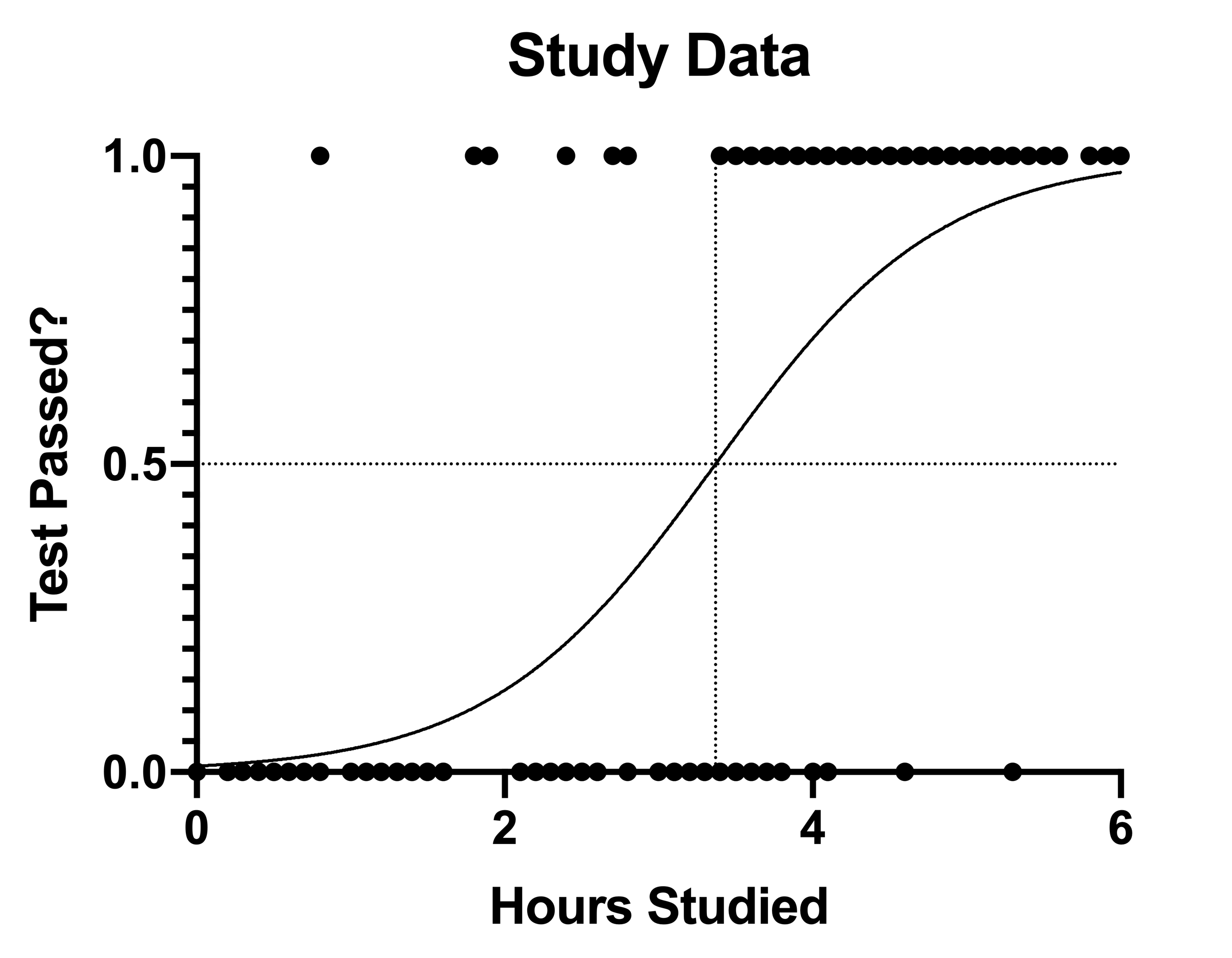


Graphpad Prism 9 Curve Fitting Guide Example Simple Logistic Regression
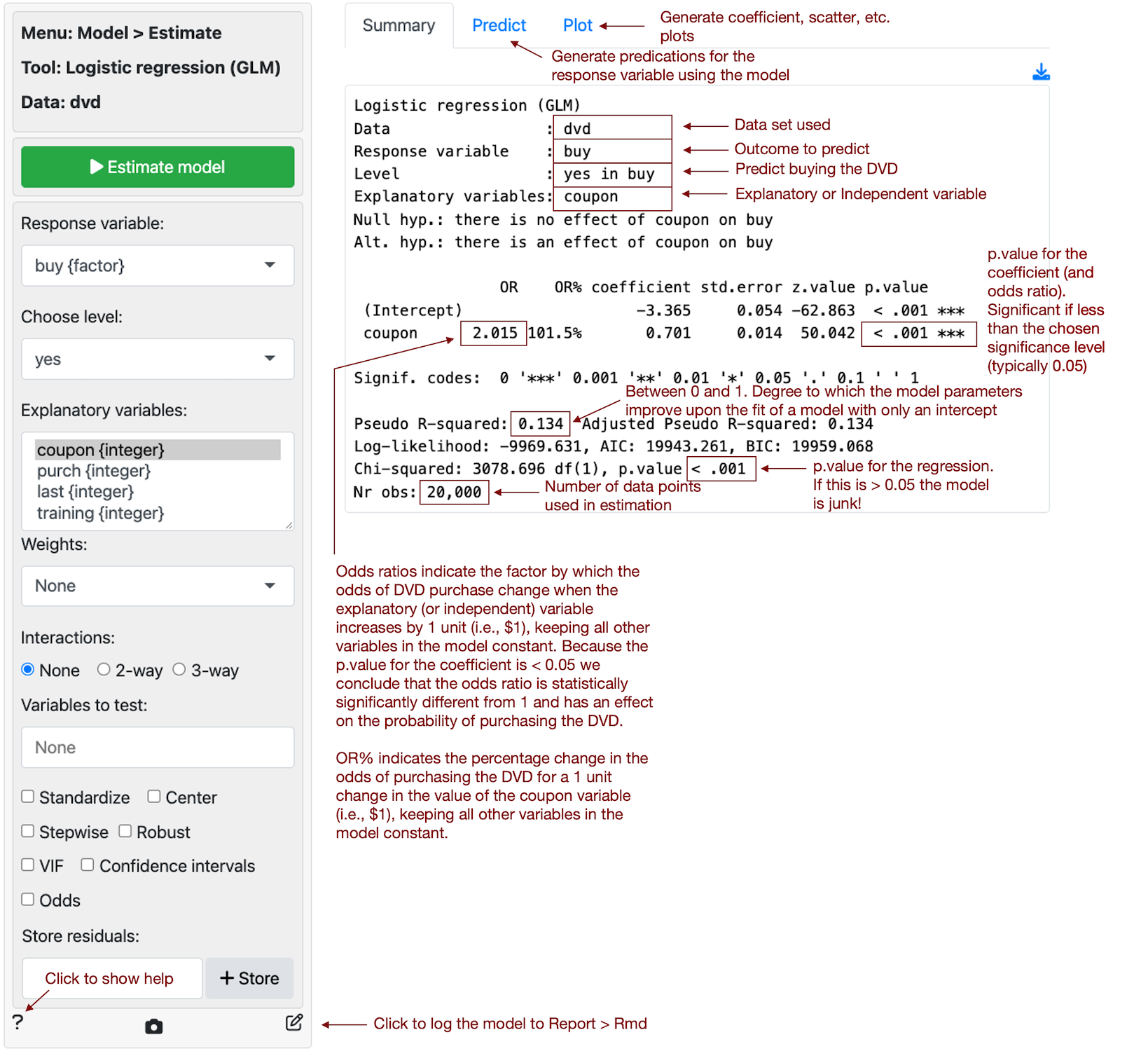


Model Estimate Logistic Regression Glm
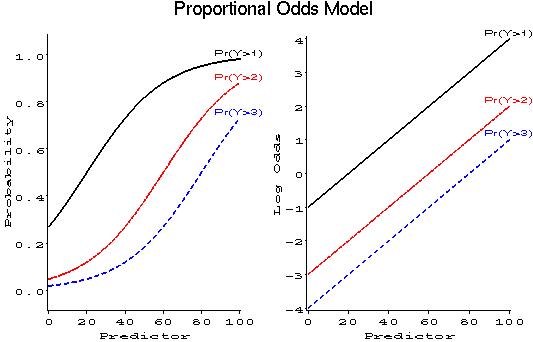


Categorical Data Part 6 Logistic Regression



Logistic Regression Coefficients And Odds Ratios Of The Probability Of Download Table



Measures Of Association Log Odds Moore Statistics Consulting Llc
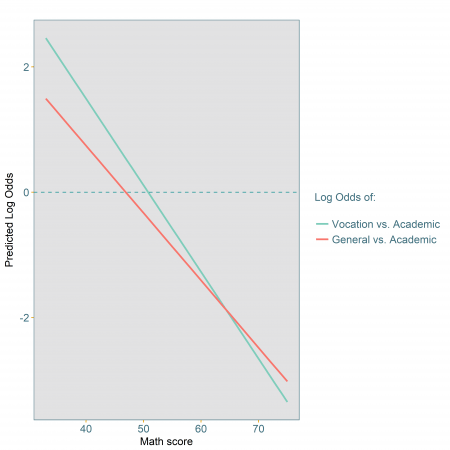


Presenting The Results Of A Multinomial Logistic Regression Model Odds Or Probabilities Select Statistical Consultants


Statquest Odds And Log Odds Clearly Explained Youtube


Understanding Logistic Regression Worldsupporter


Probability Calculation Using Logistic Regression



Proportional Odds Logistic Regression On Laef The Probability Of Download Scientific Diagram


Logistic Regression Explained Learn By Marketing



Gr S Website


Logistic Regression



Solved 21 It Is Useful To Compare A Logistic Regression Chegg Com


Logistic Regression



Binary Logistic Regression With Odds Ratios Calculated For The Download Table


Logistic Regression From Bayes Theorem Count Bayesie


Logistic Regression Multiple Logistic Odds Ratio Statsdirect



Logistic Regression Wikipedia


How To Go About Interpreting Regression Cofficients


Logistic Regression With Stata Chapter 1 Introduction To Logistic Regression With Stata



Interpreting The Impact Size Of Logistic Regression Coefficients By Ying Ma Ro Data Team Blog Medium


Odds Ratio The Odds Ratio Is Used To Find The By Analyttica Datalab Medium


What And Why Of Log Odds What Are Log Odds And Why Are They By Piyush Agarwal Towards Data Science



Logistic Regression Wikipedia



Keep Calm And Learn Multilevel Logistic Modeling A Simplified Three Step Procedure Using Stata R Mplus And Spss
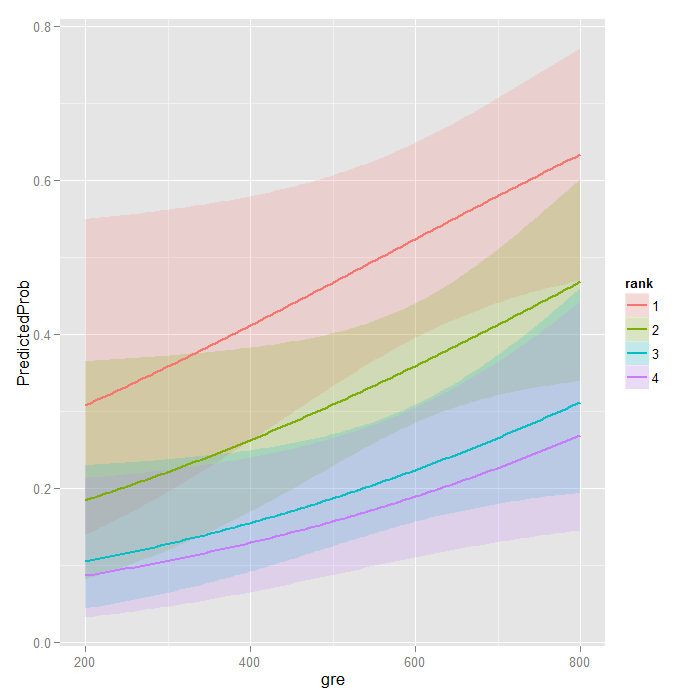


Logit Regression R Data Analysis Examples
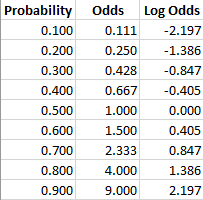


Log Odds Definition And Worked Statistics Problems



R Calculate And Interpret Odds Ratio In Logistic Regression Stack Overflow



Logistic Regression In Python An Explanation Of The Logistic By Cory Maklin Towards Data Science
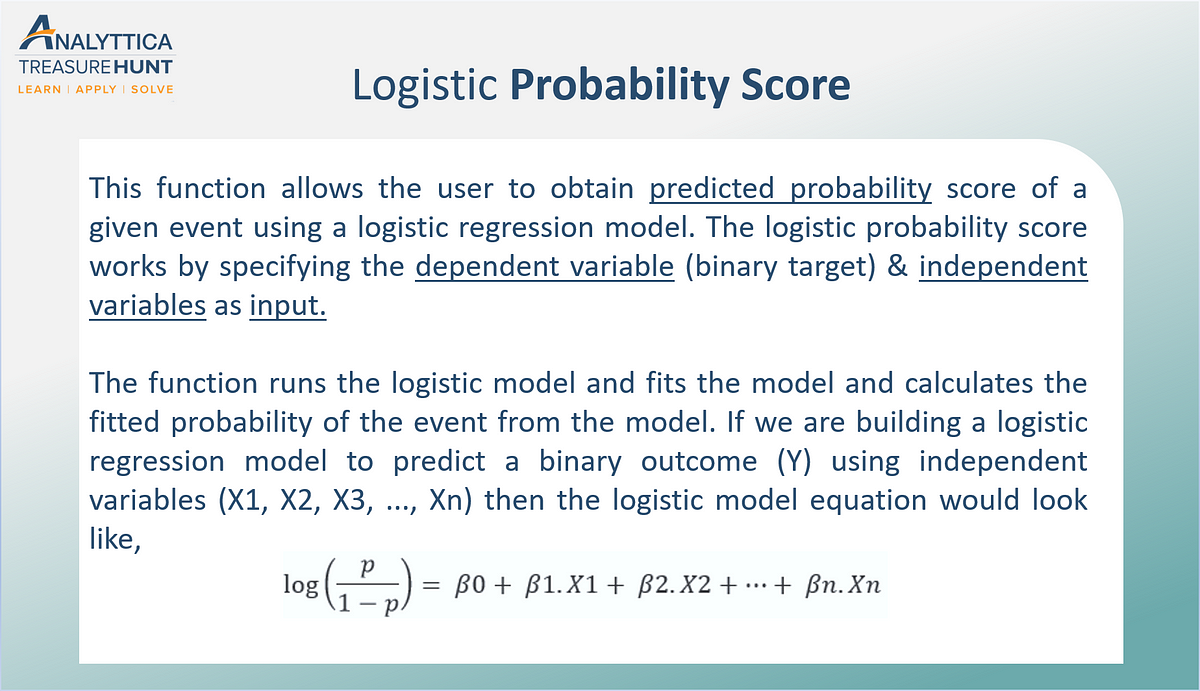


Logistic Probability Score The Logistic Probability Score Function By Analyttica Datalab Medium



Logit Of Logistic Regression Understanding The Fundamentals By Saptashwa Bhattacharyya Towards Data Science
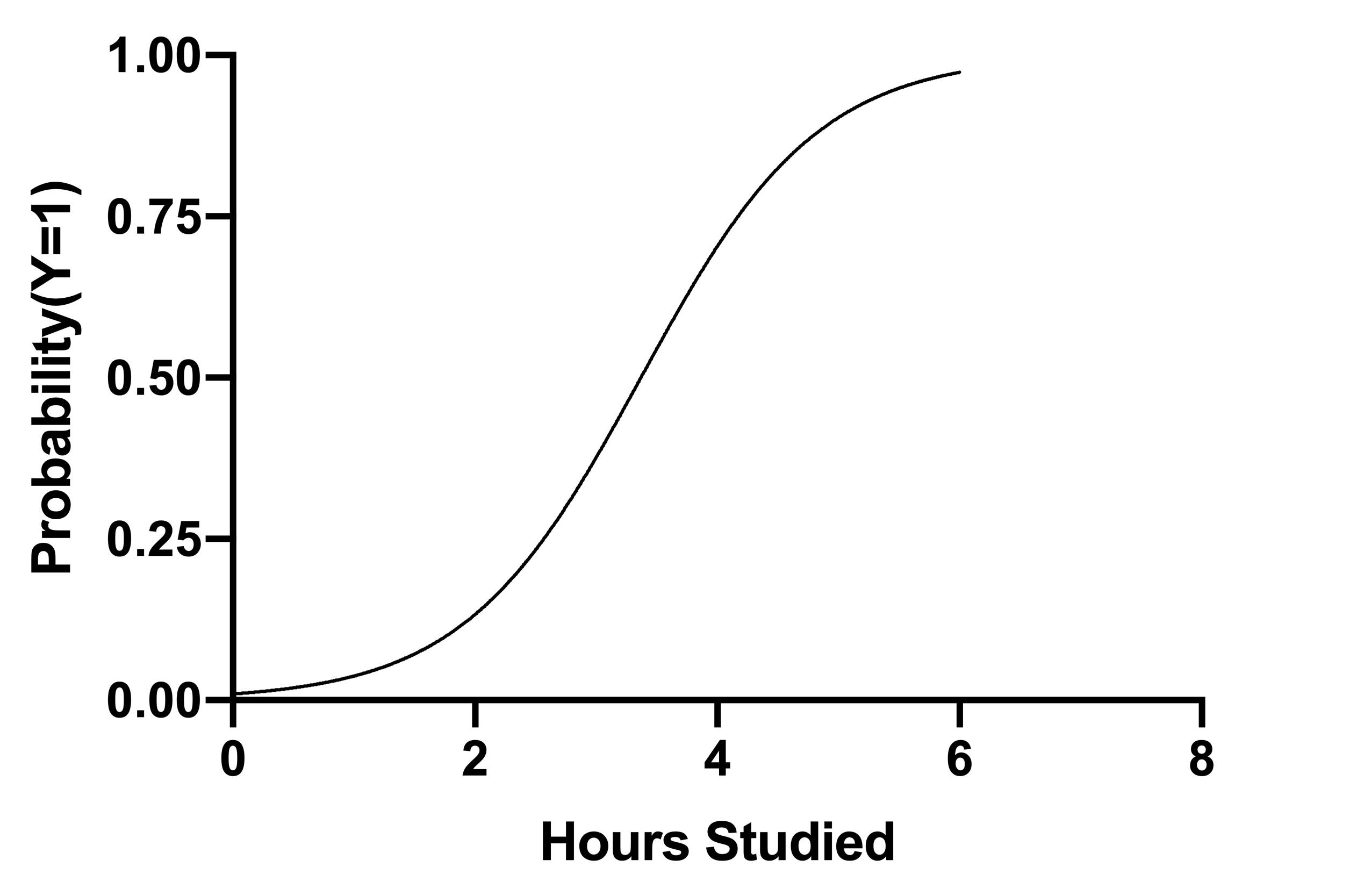


Graphpad Prism 9 Curve Fitting Guide Interpreting The Coefficients Of Logistic Regression



Logistic Regression Estimates Of The Probability Of Arranged Vs Download Scientific Diagram



Binary Logistic Regression With Odds Ratios Calculated For The Download Table
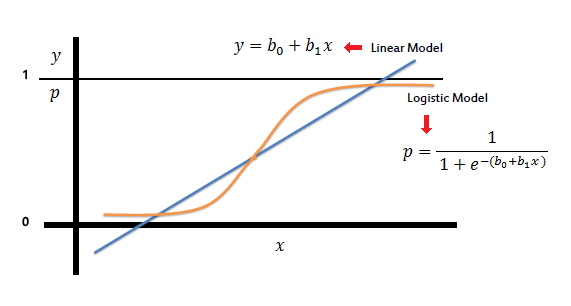


Logistic Regression
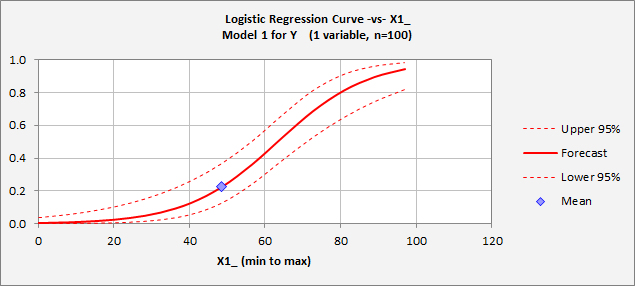


Logistic Regression In Excel Regressit


Why Saying A One Unit Increase Doesn T Work In Logistic Regression Learn By Marketing


Logistic Regression



Logistic Regression The Journey From Odds To Log Odds To Mle To Woe To Let S See Where It Ends By Rutvij Lingras Analytics Vidhya Medium


Logistic Regression



Logistic Regression Wikipedia
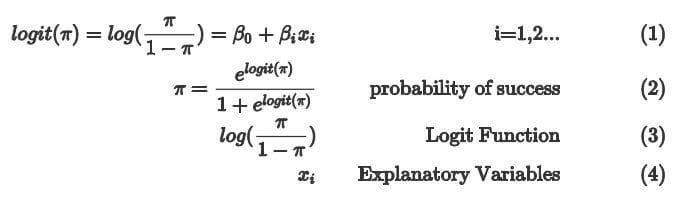


Logistic Regression A Concise Technical Overview Kdnuggets
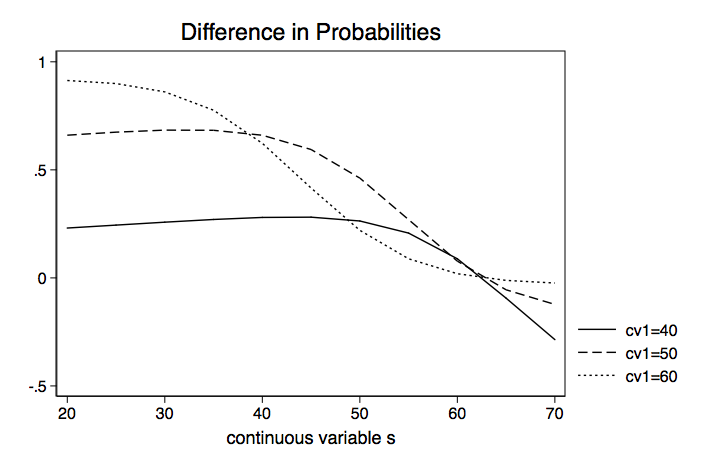


Deciphering Interactions In Logistic Regression


Logit Wikipedia


Logistic Regression Odds Ratio



Logistic Regression Wikipedia



What Is Predicted Probability Magoosh Statistics Blog



Logistic Regression In Python An Explanation Of The Logistic By Cory Maklin Towards Data Science
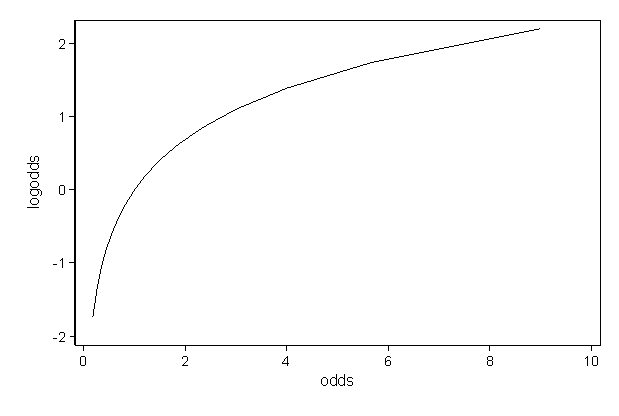


Faq How Do I Interpret Odds Ratios In Logistic Regression
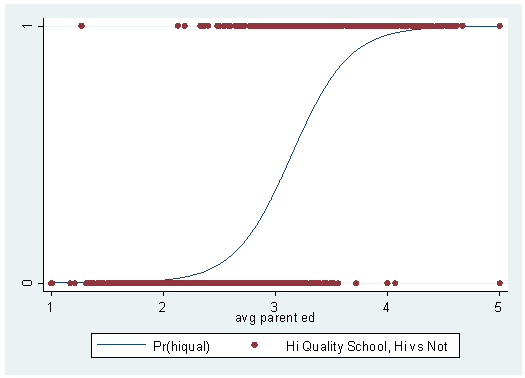


Logistic Regression With Stata Chapter 1 Introduction To Logistic Regression With Stata
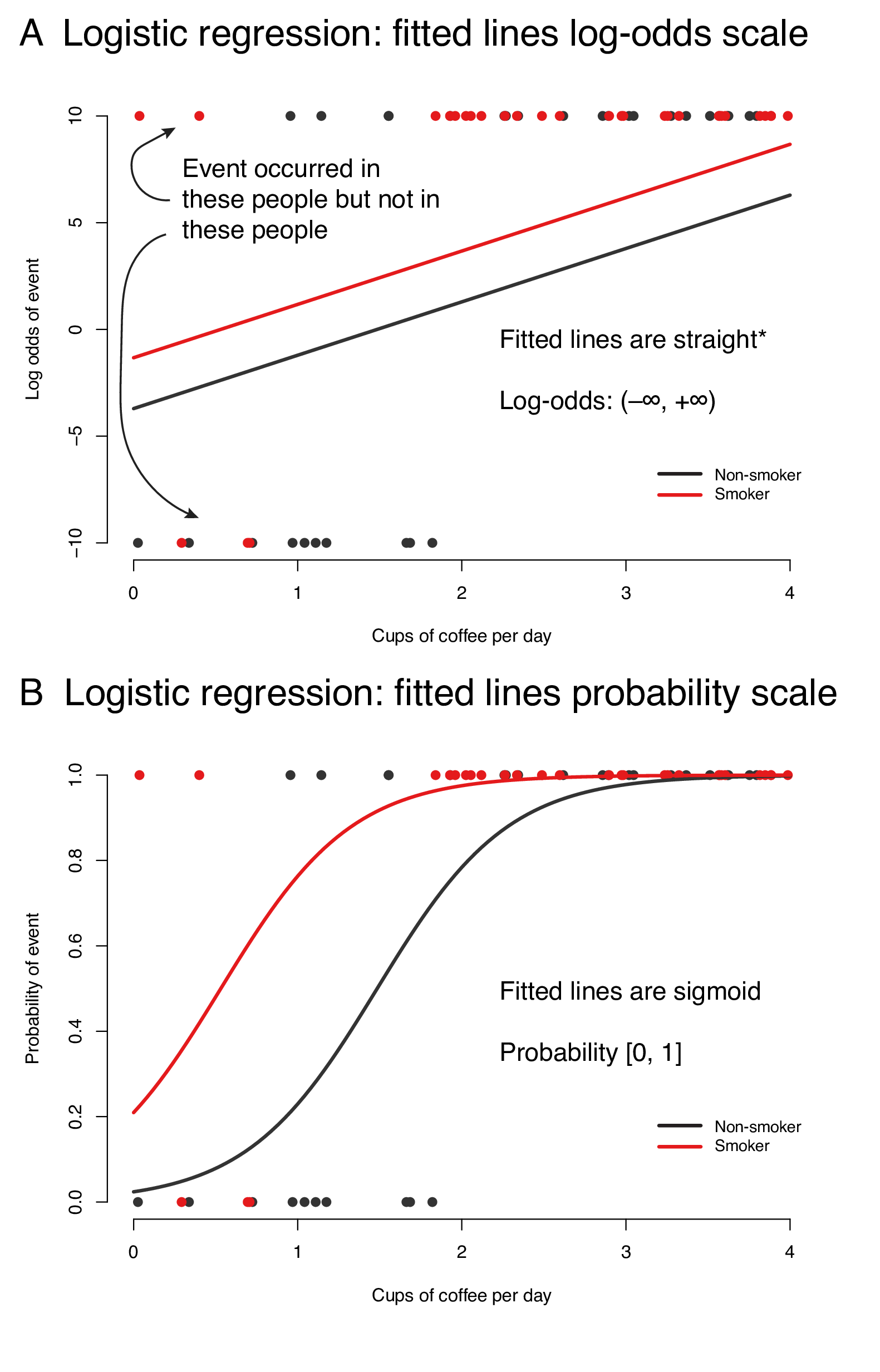


9 2 Binary Logistic Regression R For Health Data Science


An Introduction To Logistic Regression



Logistic Regression Analysis An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
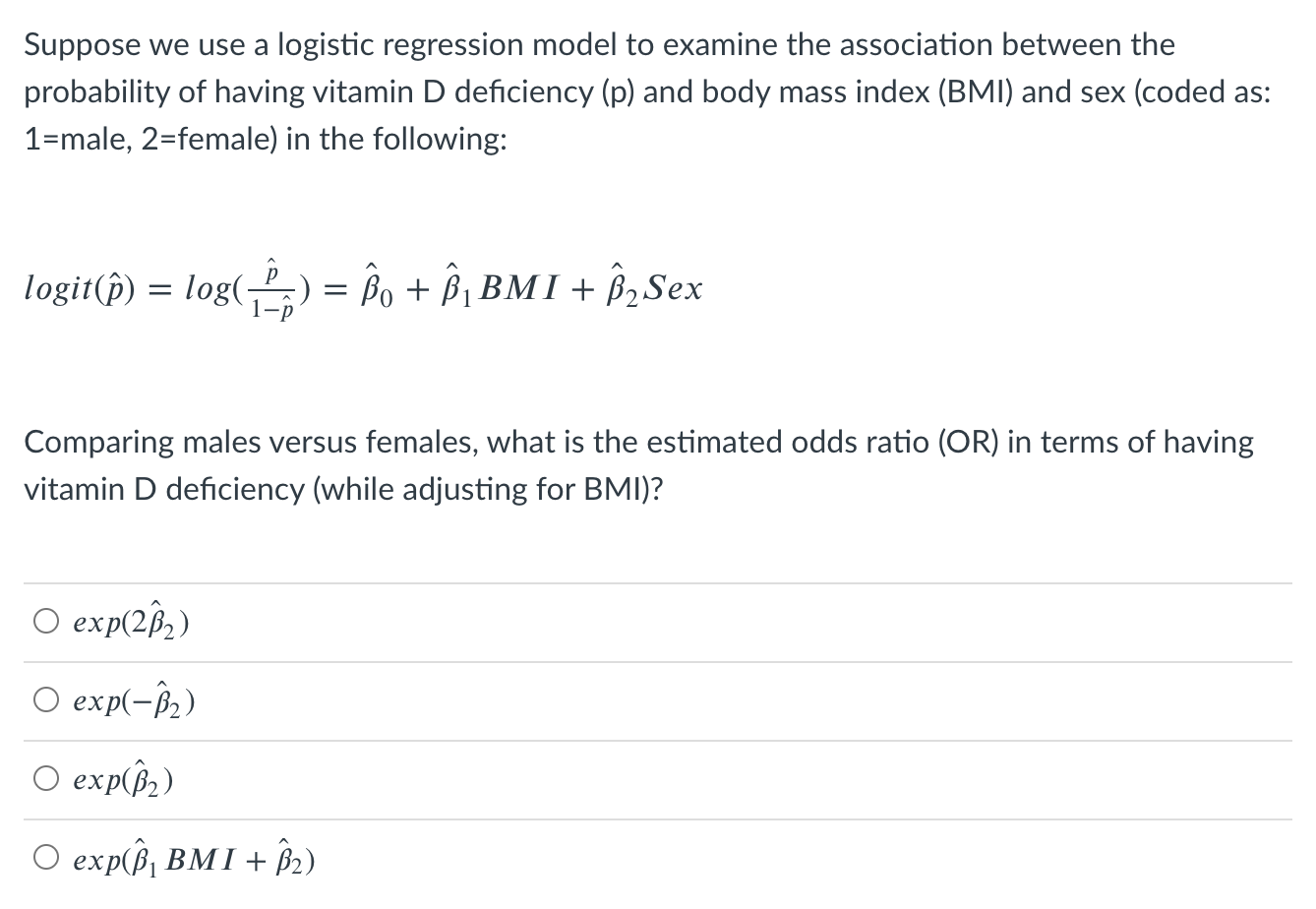


Solved Suppose We Use A Logistic Regression Model To Exam Chegg Com



Use And Interpret Logistic Regression In Spss
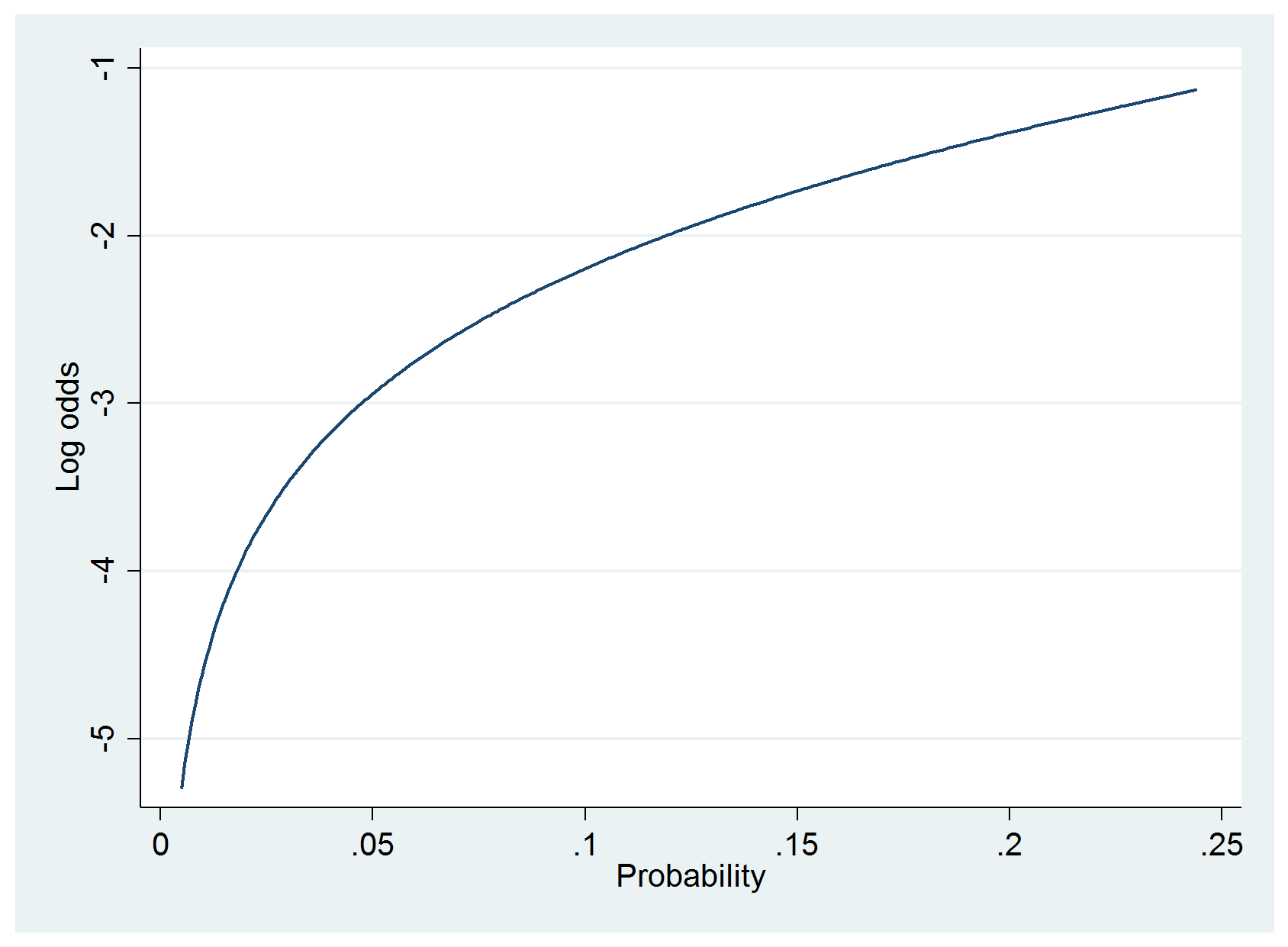


In Defense Of Logit Part 2 Statistical Horizons
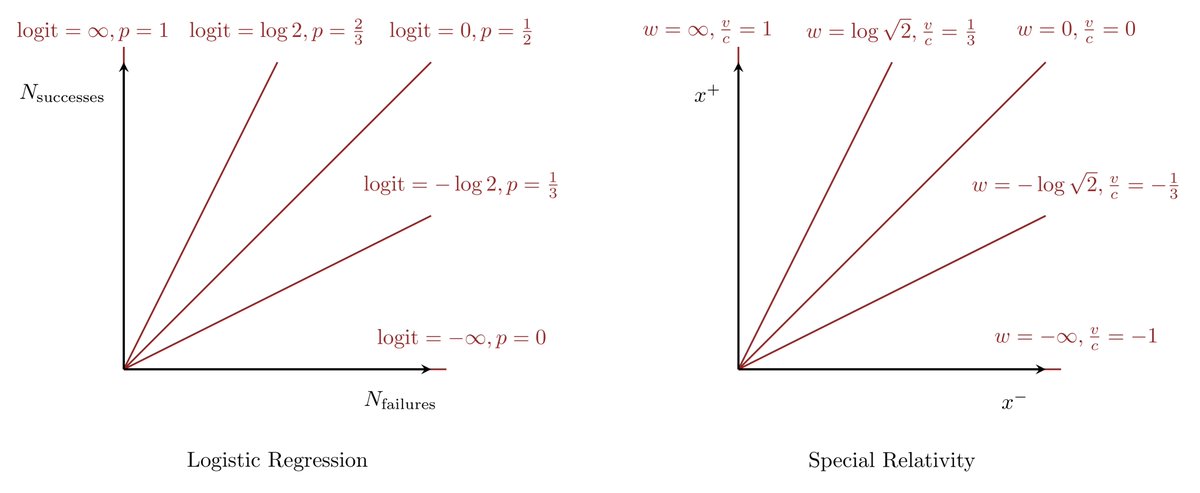


Mathfrak Michael Shapes Dude Betancourt Friendly Reminder That From A Math Perspective Probabilities In Logistic Regression Are Almost Exactly The Same As Velocities In Special Relativity If You Understand Log Odds
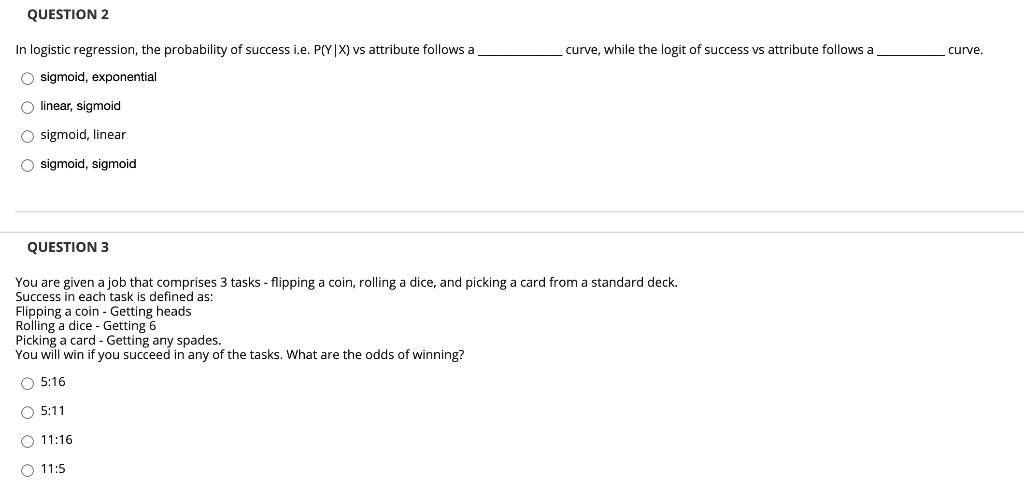


Solved Question 2 In Logistic Regression The Probability Chegg Com



Logistic Regression Circulation



No comments:
Post a Comment